応用事例
Mad City Labs, Inc.のピエゾナノポジショニングシステム、マイクロポジショニングシステム、機器ソリューション、およびピエゾアクチュエータは、さまざまな用途で使用されています。
以下のリンクから、Mad City Labsのシステムの各分野における応用例の一部をご紹介いたします。
Mad City Labs, Inc piezo nanopositioning systems, micropositioning systems, instrument solutions, and piezoactuators are used for a variety of applications. Follow the links below to learn more about how Mad City Labs systems are used in each application area.
超解像(SR)顕微鏡
超解像顕微鏡【Super-resolution (SR) Microscopy】は、Ernst Abbeによって説明された従来の回折限界を超える新たに登場したいくつかの光学顕微鏡技術を指す総称です。
従来の光学顕微鏡では約250nmの分解能が得られますが、これらのSR技術では数十ナノメートルの分解能が可能になります。
SR技術は、特定の蛍光プローブが示す光物理特性に依存しています。
これらのプローブの蛍光状態は、特定の波長の光を照射することで積極的に操作できます。
SR顕微鏡では、これらのプローブ特性を利用して、2つの近接した蛍光源から放出された光子を空間的に制限(STED、SSIM)するか、または時間的に分離(STORM、PALM)して、個別に画像化できるようにします。
これにより、回折限界を回避します。
SR技術は、ナノメートルスケールで細胞の動的な世界を前例のない形で観察する可能性を秘めています。
しかし、これらのSRイメージング技術では、イメージングシステムの安定性が非常に重要です。
SR技術が一般的に使用されるようになるにつれて、「安定性の限界」が分解能の限界として回折限界に代わる可能性があります。
Mad City Labsは、測定されたシステムドリフトの能動フィードバック補償を通じて、イメージングシステムの超高安定性を実現するために設計された製品をいくつか提供しています。
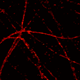
Image at left: SR microscopy (STORM) image of Cy5-Cy3 labeled tubulin from A431cells, courtesy of Prof. K. Lidke, University of New Mexico.
Super-resolution microscopy is a blanket term used to describe several newly emerging forms of light microscopy, each of which surpasses the classical diffraction limit as described by Ernst Abbe. While conventional light microscopy attains resolving power of about 250nm, these SR techniques enable resolutions of tens of nanometers.
The SR methods depend on photo-physical properties displayed by particular fluorescent probes used to mark the particular process of interest. The fluorescent state of these probes can be proactively manipulated by exposure to specific wavelengths of light. SR microscopy exploits these probe properties to either spatially restrict (STED, SSIM), or temporally separate (STORM, PALM) the photons emitted by two closely spaced fluorescent sources so that they can be imaged separately, and in doing so circumvents the diffraction limit.
The SR methods show great promise to enable unprecedented views into the dynamic world of the cell at the nanometer scale. However, these SR imaging techniques place a great premium on the stability of the imaging system, and as the SR methods make their way into common use, a “stability limit” may replace the diffraction limit on resolving power.
Mad City Labs offers several products designed to achieve ultra-high stability in an imaging system through active feedback compensation of measured system drift.
超解像(SR)顕微鏡について詳しくは専用ページをご確認ください。
蛍光顕微鏡および分光法
Mad City Labsの多軸ピエゾナノポジショニングサンプルステージ、対物レンズナノポジショナー、マイクロポジショニングステージ、およびC-Focus顕微鏡安定化システムは、Förster共鳴エネルギー移動(FRET)イメージング、蛍光寿命イメージング顕微鏡(FLIM)、共焦点顕微鏡、コヒーレント反ストークスラマン分光法(CARS)、全内部反射蛍光(TIRF)イメージング、光漂白後蛍光回復(FRAP)イメージングなどの蛍光検出技術に使用されています。
Mad City LabsのMicroMirror TIRF顕微鏡は、対物レンズを通じた励起を行いますが、従来のTIRFMシステムで使用されるダイクロイックミラーを、対物レンズのバックアパーチャの反対側の縁に配置された2つの広帯域マイクロミラーに置き換えています。
この照明方法により、励起経路と発光経路が空間的に分離され、ダイクロイックミラーを使って分光的に分離する必要がなくなります。マルチバンドダイクロイックミラーは、透過特性が大幅に低下し、それによって生じる光子損失によりマルチカラー実験のパワーが制限されます。
マルチバンドダイクロイックミラーを排除することで、MicroMirror TIRF顕微鏡システムは、3色以上の蛍光体を使用した単一分子分析に必要な優れた光子感度と信号対雑音比を実現します。
Nature Protocolsは、ウィスコンシン大学マディソン校およびブランダイス大学の研究者が、MicroMirror TIRFシステムを使用した細胞機械の研究に用いる「共局在単一分子分光法(CoSMoS)」法に関する論文を発表しました。
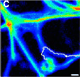
Image at left from Valeria Levi, Anna S Serpinskaya, Enrico Gratton, and Vladimir I Gelfand. Organelle transport along microtubules in
Xenopus melanophores: evidence for cooperation between multiple motors. Biophys J. 2006; 90(1): 318-27. Figure 5(c).
Mad City Labs’ multi-axis piezo nanopositioning sample stages, objective lens nanopositioners, micropositioning stages, and C-Focus microscope stabilization system are being used for fluorescence detection techniques including Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) imaging, fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM), confocal microscopy, coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy (CARS), total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) imaging, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) imaging, and others.
Mad City Labs’ MicroMirror TIRF microscope uses through-the-objective excitation, but replaces the dichroic mirror used in conventional TIRFM systems with two broadband micromirrors positioned at opposite edges of the back aperture of the objective lens. This illumination method enables the spatial separation of the excitation and emission pathways, eliminating the need to spectrally separate them using a dichroic mirror. Multi-band dichroic mirrors have substantially reduced transmission properties that limit the power of multi-color experiments through the resulting photon losses. By eliminating multi-band dichroic mirrors, our MicroMirror TIRF microscopy system yields the superior photon sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratios required for single molecule analyses using three or more fluorophores.
Nature Protocols has published a paper from researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and Brandeis University about the colocalization single-molecule spectroscopy (CoSMoS) method for studying cellular machines using the MicroMirror TIRF system.
走査型プローブ顕微鏡法および表面プロフィロメトリー
走査型プローブ顕微鏡(SPM)は、物理的なプローブを使用してサンプルを走査し、表面の画像を形成する顕微鏡技術のカテゴリを指します。一般的に使用されるプローブの例として、タングステンチップや秋山プローブがあります。
プローブをサンプルのラスタースキャンで機械的に移動させ、位置に応じたプローブと表面の相互作用を記録することで、表面の画像が得られます。多くのSPM技術では、SPM機器に使用されるピエゾアクチュエータによる動作制御の特性により、原子レベル、さらにはサブ原子レベルの解像度が達成できます。
Mad City Labsは、原子間力顕微鏡(AFM)、近接場光学顕微鏡(NSOM)、その他のSPM用途に適した高解
像度のクローズドループピエゾナノポジショニングシステムを提供しています。また、最近開発した製品「MadPLL®」は、さまざまな環境で使用できる、堅牢で低コストなSPMシステムを構築する能力をユーザーに提供します。

Image at left generated from Data taken using MadPLL® with Nano-OP30 nanopositioning system (Z-axis), Nano-OP100nanopositioning system (XY axes): Fly eye, 100µm x 100µm bidirectional scan, PLL mode, constant probe signal, Z forcefeedback: frequency.
走査型プローブ顕微鏡(SPM)は、物理的なプローブを使用してサンプルを走査し、表面の画像を形成する顕微鏡技術のカテゴリを指します。
一般的に使用されるプローブの例として、タングステンチップや秋山プローブがあります。プローブをサンプルのラスタースキャンで機械的に移動させ、位置に応じたプローブと表面の相互作用を記録することで、表面の画像が得られます。多くのSPM技術では、SPM機器に使用されるピエゾアクチュエータによる動作制御の特性により、原子レベル、さらにはサブ原子レベルの解像度が達成できます。
Mad City Labsは、原子間力顕微鏡(AFM)、近接場光学顕微鏡(NSOM)、その他のSPM用途に適した高解
像度のクローズドループピエゾナノポジショニングシステムを提供しています。また、最近開発した製品「MadPLL®」は、さまざまな環境で使用できる、堅牢で低コストなSPMシステムを構築する能力をユーザーに提供します。
Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) refers to a category of microscopy techniques that form images of surfaces using a physical probe that scans a sample. Examples of commonly used probes are tungsten tips and the Akiyama probe. An image of the surface is obtained by mechanically moving the probe in a raster scan of the sample and recording the probe-surface interaction as a function of position. Atomic, and even sub-atomic, resolution can be achieved by many SPM techniques largely due to the characteristics of the piezo-actuated motion control used in SPM instruments.
Mad City Labs offers high-resolution, closed loop piezo nanopositioning systems well suited to atomic force microscopy (AFM), near field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM), and other SPM applications. Our recently developed product, MadPLL®, offers users the ability to assemble a robust, inexpensive SPM system for use in a variety of environments.
光ピンセット&光トラップ
光ピンセットは、強く集束されたレーザービームを介して、ナノメートルおよびミクロンサイズの誘電体粒子に対して]極めて小さな(ピコニュートン単位の)力を加え、操作することができます。
光トラップは非常に感度の高い機器であり、サブミクロンの誘電体粒子に対してサブナノメートルの変位を操作および検出することが可能です(参考: Moffitt JR, Chemla YR, Izhaky D, Bustamante C [2006]. 二重トラップの差動検出により光ピンセットの空間分解能が向上。Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103(24): 9006–9011.)。これらは、分子に結合したビーズと相互作用することにより、単一分子の操作や研究に使用されてきました。
この方法でDNAや、それに相互作用するタンパク質や酵素が研究されています。
ほとんどの光トラップは、誘電体粒子がトラップの中心から大きく移動しないように操作されます。
その理由は、粒子に加えられる力が、中心からの変位が小さい限り、変位に対して線形になるためです。
このように、光トラップはフックの法則に従う単純なばねと比較できます。粒子の位置は、試料を精密に移動させるか、トラップ自体を移動させることで維持できます。
Mad City Labsは、粒子が中心に留まるようにするサブナノメートル精度のピエゾナノポジショニングシステムや、レーザービームの経路を制御し、光トラップの位置を操作できるビームステアリングナノポジショニングシステムを製造しています。
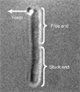
Image at left from Wang, S., Arellano-Santoyo, H., Combs, P.A., Shaevitz, J.W. Actin-like cytoskeleton contributes to cell mechanics in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107(20):9182-9185 (2010). Figure 1(b)
Optical tweezers are capable of manipulating nanometer and micrometer-sized dielectric particles by exerting extremely small (piconewton) forces via a highly focused laser beam. Optical traps are very sensitive instruments and are capable of the manipulation and detection of sub-nanometer displacements for sub-micron dielectric particles. (Ref. Moffitt JR, Chemla YR, Izhaky D, Bustamante C [2006]. Differential detection of dual traps improves the spatial resolution of optical tweezers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (24): 9006–9011.) They have been used to manipulate and study single molecules by interacting with a bead that has been attached to that molecule. DNA and the proteins and enzymes that interact with it have been studied in this way.
Most optical traps are operated such that the dielectric particle rarely moves far from the trap center. The reason for this is that the force applied to the particle is linear with respect to its displacement from the center of the trap provided the displacement is small. In this way, an optical trap can be compared to a simple spring, which follows Hooke’s law. The particle position can be maintained by either precisely moving the sample or moving the trap itself.
Mad City Labs produces piezo nanopositioning systems with sub-nanometer precision that enable the particle to remain centered and beam steering nanopositioning systems which can control the laser beam path and hence the location of the optical trap.
磁気ピンセット、磁気トラップ、磁気マニピュレーション
Mad City Labsは、磁気ピンセット、磁気トラップ、磁気操作用の単軸および多軸ピエゾナノポジショニングシステムを提供しています。
当社の製品ラインには、高速システム、開口部を備えたシステム、高い力や負荷に対応するシステムなど、多くの異なる形状や機能を持つピエゾステージが含まれています。

Image at left from Fisher, J.K., J. Cribb, K.V. Desai, L. Vicci, B. Wilde, K. Keller, R.M. Taylor, J. Haase, K. Bloom, E.T. O’Brien, and R. Superfine.
Thin-foil magnetic force system for high-numerical-aperture microscopy. Rev Sci Instrum. 2006. 77(2): 023702-1–023702-9. Figure 8 [inset].
Mad City Labs offers single and multi-axis piezo nanopositioning systems for magnetic tweezers, magnetic traps, and magnetic manipulation. Our product line consists of piezo stages with many different form factors and features, including high speed systems, systems with apertures, and systems for high force or load.
ナノファブリケーション、ナノパターニング、ナノマシニング
Mad City Labsのピエゾナノポジショニングシステムおよびマイクロポジショニングシステムは、ナノファブリケーション、ナノパターニング、ナノマシニングに使用されています。
Nano-Align3シリーズ、Nano-Align5シリーズ、Nano-Align6シリーズは、複数軸の線形ポジショニングに加えて、
ティップ、チルト、または回転の複数軸を提供し、ナノメートル精度での正確なアライメントとポジショニングを可能にします。また、Mad City Labsは、特殊用途向けの高速かつ高負荷対応のシステムも製造しています。

Image at left of 100µm square pattern created by modification of glass structure by non-linear
absorption of femtosecond laser, courtesy of Y. Bellouard and Femtoprint.
Mad City Labs piezo nanopositioning systems and micropositioing systems are used for nanofabrication, nanopatterning, and nanomachining. The Nano-Align3 Series, Nano-Align5 Series, and Nano-Align6 Series provide multiple axes of linear positioning along with multiple axes of tip, tilt, or rotation to make parallel alignment with nanometer precision possible for accurate alignment and positioning. Mad City Labs also manufactures high speed and high load systems for special applications.
その他のアプリケーション
Mad City Labsのピエゾナノポジショニングシステム、マイクロポジショニングシステム、統合システム、および機器ソリューションは、さまざまな用途に使用されています。
これらの用途の一部として、光アンテナとナノオプティクス、高スループットイメージング、位相シフト干渉計、粒子加速器のビームプロファイリング、アクティブおよびアダプティブオプティクス、リソグラフィー、MEMSおよびNEMSテストが含まれます。

Image at left from Myun-Sik Kim, Toralf Scharf, and Hans Peter Herzig. Small-size microlens characterization by multiwavelength high-resolution
interference microscopy. Opt. Express 18, 14319-14329, 2010. Figure 4(a).
Mad City Labs’ piezo nanopositioning systems, micropositioning systems, integrated systems, and instrument solutions have been used for a variety of other applications. A small sampling of these applications includes Optical Antennas and Nano-Optics, High Throughput Imaging, Phase Shift Interferometry, Particle Accelerator Beam Profiling, Active and Adaptive Optics, Lithography, and MEMS and NEMS testing.
